We were talking about subsurface oil in the Gulf when she said matter-of-factly, "The bacteria are running amok with the dispersants." What? "Those oil-eating bacteria -- I think they're running amok and causing skin rashes." My mind reeled. Could we all have missed something so simple?
The idea was crazy but, in the context of the Gulf situation -- an outbreak of mysterious persistent rashes from southern Louisiana across to just north of Tampa, Florida, coincident with BP's oil and chemical release, it seemed suddenly worthy of investigating.
I first heard about the rash from Sheri Allen in Mobile, Alabama. Allen wrote of red welts and blisters on her legs after "splashing and wading on the shoreline" of Mobile Bay with her two dogs on May 8. She reported that "hundreds of dead fish" washed up on the same beach over the following two days. This was much too early for the summer sun to have warmed the water to the point of oxygen depletion, but not too early for dispersants and dispersed oil to be mixed into the Gulf's water mass. By early July, Allen's rash had healed, leaving black bruises and scarring.
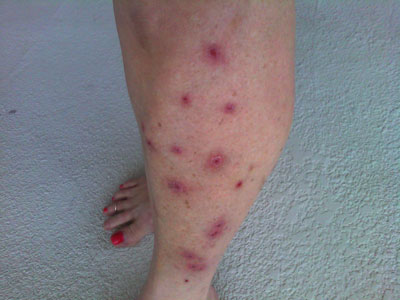
A mysterious persistent skin rash has occurred across the Gulf, coincident with BP's release of oil and chemical dispersants. Mobile, Alabama, resident Sheri Allen was one of the first to report its occurrence in early May. (Photo: Sheri Allen)
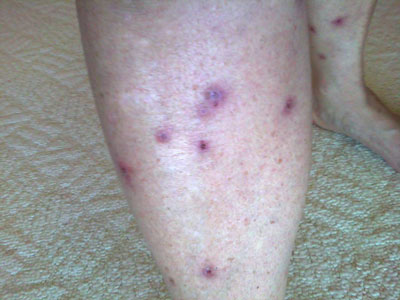
Sheri Allen's rash had largely healed by July 2, leaving bruises and scarring, similar to other reports across the Gulf. (Photo: Sheri Allen)
Other people -- both residents and visitors to the Gulf Coast -- wrote of similar rashes or other skin problems like peeling palms. The rashes have been diagnosed as scabies and staph infections, including MRSA, the potentially lethal Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Most cases lingered for months, as the rash did not respond well to antibiotics, steroid creams, or steroid shots.
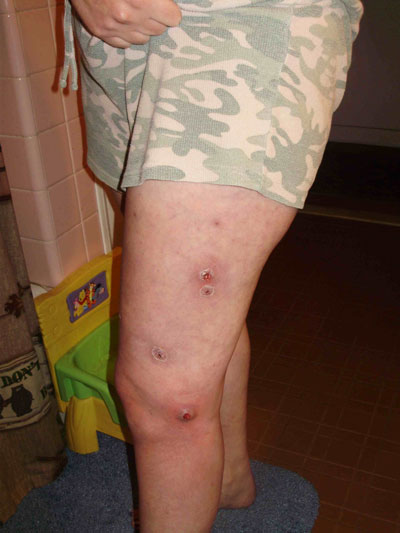
Medical doctors are diagnosing skin rashes on Gulf visitors and residents alike as scabies and staph infections, including MRSA (this photo, identity protected). The rashes resist prescribed treatments and often reoccur for months. (Photo permission: Riki Ott)
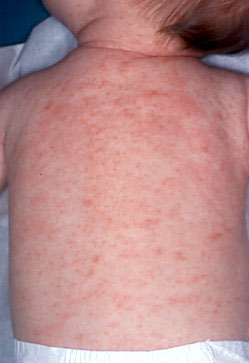
Normal looking scabies contrasts sharply with the Gulf cases. (Photo: provided by Nurse Ali Schmidt)
That should have been a clue that maybe the primary cause was not biological, but chemical. A secondary biological infection might clear up with antibiotic treatment, but then keep reoccurring because the primary chemical illness had not been treated.
Retired Registered Nurse Allison Schmidt agrees. Referring to Allen's case, she said, "I can say without hesitation that these skin rashes have nothing to do with scabies. Scabies is a parasite, which causes a skin infection and is extremely contagious. It spreads from person to person by direct skin contact or by wearing an article of clothing worn by an infected person." Schmidt said, "If this were scabies you would see entire families infected and NOT just a single family member."
Another clue to the real cause of the mystery rash is its prevalence across the entire oil-impacted Gulf. Something in the water or air, or both, could explain this. While public officials and BP claim that dispersant use was halted in May for Corexit 9527A and on July 19 for Corexit 9500A, evidence collected by Gulf residents has shown that dispersants are being used in nearshore and inland waters, close to highly populated areas across the Gulf. Further, oil and the Corexit marker have been found in air and inland water.

Despite denial by public officials and BP, evidence mounts of continued dispersant use in inland and nearshore waters near populated areas across the Gulf. Private contractor in Carolina Skiff with tank of Corexit dispersant, August 10, south of Pass Christian Harbor, Mississippi, 9:30 AM. (Photo: Don Tillman)
I have heard from Gulf residents and visitors who developed a rash or peeling palms from contact with Gulf water, including such activities as swimming or wading, getting splashed, handling oiled material or dead animals without gloves, and shucking crabs from the recently opened Gulf fisheries. I have also heard from people who developed the same symptoms after contact with Gulf air by wiping an oily film off their airplane's leading edges after flying over the Gulf (absorbent pad tested positive for oil) or swimming in outdoor pools, or splashing in puddles, after it rained.
Outraged by the unprecedented release of oil and toxic chemicals in the Gulf, Nurse Schmidt and Mike McDowell developed a project to test Gulf rainwater for harmful chemicals. Schmidt said, "We are convinced the chemicals used in the Gulf to help disperse oil have evaporated and will eventually come down mixed with the rain."
Another clue, more like a condemnation, is that NOAA and EPA decided to use dispersants in the Gulf without considering what harm the chemicals and dispersed oil might do to people, specifically, the general public. Dr. Sylvia Earle, former chief scientist of NOAA, and other scientists, criticized the agencies' decision, in part, based on concern about harm to human health. Other scientists have also criticized the agencies' decision. Citing the National Academy of Sciences, a Texas Tech University professor testified in Congress that the chemicals break down cell walls, making organisms (including people) more susceptible to oil. The professor called the Gulf an "eco-toxicological experiment," which is inexcusable, because OSHA has known about harm from solvent exposure since at least 1987. Don't these federal agencies talk amongst themselves -- or with others?
Which all brings me back to the grandmother. After talking with her, I've been reading about bacteria, and I now think the Great Gulf Experiment is going very badly for humans. One can only wonder about the rest of the ecosystem.
There are two distinct types of bacteria based on the structure of their cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria have a single-membrane cell wall, while Gram-negative bacteria have a double-membrane cell wall. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria are "Gram-positive," while the oil-eating bacteria are Gram-negative.
But! A component of the double-membrane cell wall structure of Gram-negative bacteria can irritate human skin, causing inflammation and activating the immune system. In other words, oil-eating bacteria, just because they are Gram-negative, can cause skin rashes. In the case of Alcanivorax borkumensis, the reaction can erupt on the skin like MRSA infections.
To make things a little scarier, some of the oil-eating bacteria have been genetically modified, or otherwise bioengineered, to better eat the oil -- including Alcanivorax borkumensis and some of the Pseudomonas. Oil-eating bacteria produce bio-films. According to Nurse Schmidt, studies have found that bio-films are rapidly colonized (p. 97) by other Gram-negative bacteria -- including those known to infect humans.
Scientists anticipated early on that the Gulf leak would cause populations of oil-eating bacteria to soar. Still, infections are not likely in healthy people. However, exposure to oil weakens a person's immune system function, as does the mental stress of dealing with disaster trauma. And then there are people who are more at risk than others to bacterial infections, especially when first challenged with oil and solvent exposure. This includes children, people with cystic fibrosis or asthma, and African Americans (who are prone to blood disorders), to name a few.
Is this the perfect storm -- an exploding population of opportunistic Gram-negative bacteria (some natural, some not), millions of gallons of food (oil) for the bacteria, and a susceptible population of stressed-out people?
Perhaps. If the outbreak of skin rashes across the Gulf is any indication, the health care providers, media, and Congress ought to be taking a hard look at this question. Further, people ought to be connecting the dots to illnesses that surfaced in Exxon Valdez spill responders and to the illnesses occurring now in Michigan residents coping with the Enbridge oil pipeline spill.
In the Gulf, Nurse Schmidt believes:
This is like a major bacterial storm. It could be the reason we are seeing a variance of symptoms in different individuals. In some people, we see respiratory complications, while in others we see skin or GI symptoms. I think it is due to a multitude of colonized bacteria -- which may have been triggered by BP's disaster.The nurse and I think the grandmother is onto something.

















